Integrating Tools with the SSS
Main impacts
- The SSS provides client-side tool developers with an easy-to-use service framework for informal learning at the workplace.
- The SSS enhances the participation of learners via providing services for sharing resources with other users in the system.
Providing the Social Semantic Server (SSS) as an open-source framework to equip client-side tools with services to support and scale informal learning at the workplace.
The situation before Layers
Highlights
Informal learning at the workplace covers a multitude of processes. Respective activities can be categorized into multiple perspectives on informal learning, such as reflection, sensemaking, help seeking and maturing of collective knowledge. Each perspective raises requirements with respect to the technical support, this is why an integrated solution relying on social, adaptive and semantic technologies is needed.
Description
Informal learning at the workplace typically accompanies everyday work processes and tasks. This kind of learning is highly individualized and related to the current problem or challenge the worker is faced with and deeply bound to the respective work context. Hence, informal learning happens on demand, in a specific context and has an episodic and informal character [1].
While on the one hand, its individual, context-bound nature makes it highly effective and motivating, on the other hand, informal learning at the workplace and its usual one-to-one training brings benefit to relatively few workers. This hinders scaling of informal learning at the workplace, and that is why suitable tools are needed to fill this gap. Available learning technologies yet often follow formal training models that are based on teacher-centered training delivered in classrooms or courses. Simply transferring these approaches to the screen does not lead to the desired outcome as it is based on a fixed curriculum and not adaptable to the current situation and context, which is needed to support informal workplace learning.
This is why an integrated solution relying on social, adaptive and semantic technologies is needed [2].
What Layers did
Highlights
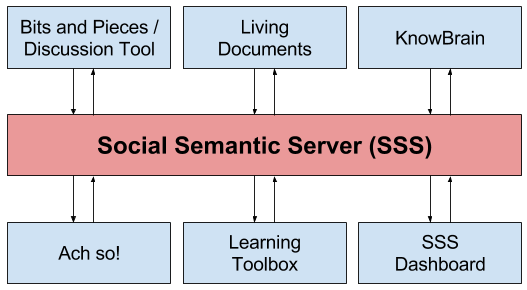
We developed the SSS as a flexible open-source framework that provides Layers tools with powerful backend functionalities. To date, six tools developed in the Layers project are supported by services of the SSS and some of them are integrated to complex tool suites via the SSS. This includes Bits & Pieces / Discussion Tool, LivingDocuments, Ach so!, Learning Toolbox, SSS Dashboard and KnowBrain.
Description
In the Layers project, we designed and developed the Social Semantic Server (SSS) as a flexible technical open-source backend infrastructure to develop tools and applications to support informal learning at the workplace. The SSS has been conceptualized and designed based on insights gained from relevant theories such as distributed cognition and meaning making. Specifically, we translated the requirements, which we identified to support informal learning at the workplace, to a set of design principles, and consequently, to set of service categories implemented in the SSS [2].
The functionalities of the SSS are divided into fine granular services that can be easily maintained, tested, reused and combined to new and more complex functionalities. As such, providing new functionalities or extending existing implementations is fostered by a lightweight service layout. Currently, the SSS provides metadata (e.g., tagging), activity (e.g., trace interactions), search (e.g., by tags or content), recommendation (e.g., tags or resource suggestions), discussion (e.g., Q&A), access restriction (e.g., groups or circles) and aggregation (e.g., learning episodes) services.
As shown in Figure 1, the resulting services are exploited in various Layers tools (Bits and Pieces - Discussion Tool, LivingDocuments, Ach so!, Learning Toolbox, SSS Dashboard and KnowBrain) that support different perspectives on informal learning. These tools are either completely based on the SSS (e.g., Bits & Pieces / Discussion Tool) or use services of the SSS (e.g., Learning Toolbox). Moreover, some of these tools are integrated to complex tool suites via the SSS (e.g., Bits & Pieces / Discussion Tool and LivingDocuments form the Healthcare Suite).
This demonstrates that the SSS is capable of supporting and integrating different informal learning practices that occur at the workplace.
The situation after Layers
Highlights
By using the services of the Social Semantic Server (SSS), developers of informal learning tools are given the possibility to focus on increasing the usability of their tools rather than focusing on the development of an own backend solution. Furthermore, the SSS fosters the integration of these tools by common services, which supports the scaling of informal workplace learning beyond the immediate context. The SSS is open-source software and freely available via Github.
Description
The community is now provided with a flexible open-source framework that can be used to equip client-side tools with services to support informal learning at the workplace. Thus, developers of such tools are given the possibility to focus on increasing the usability of their tools rather than focusing on the development of an own backend solution. Via its service-based architecture, the Social Semantic Server (SSS) can be flexibly set up for the needs of each tool developer (e.g., deploy the Social Semantic Server (SSS) only with a subset of its services).
Additionally, the data collected in the Social Semantic Server (SSS) can be used for different kinds of applications in the area of Learning Analytics such as exploiting the data for Tag Recommender Services, Resource Recommender Services and Consensus Building Services, or visualizing the data in dashboards (e.g., the SSS Dashboard).
Finally, the community has now access to six tools in the area of informal workplace learning, which exploit services and/or data of the SSS (see Figure 1). In this respect, the SSS also fosters the integration of these tools by common services, which supports the scaling of informal workplace learning beyond the immediate context.
Impact that Layers created
Changed learning practices
The SSS enhances the participation of learners via providing services for sharing resources with other users in the system. This functionality also fosters the co-creation of learning materials in personal networks.
Extended trust building and personal networks
The SSS supports learners in extending trust building and relationships via its access restriction and group services. Thus, the SSS allows to create so-called circles (e.g., as known from Google+), in which resources and users can be grouped to personal learning networks.
Improved the creation and use of learning resources
Since the SSS enables the upload of any kind of resource (e.g., images, Web links, documents or even Evernote notes), it supports the production of learning resources either individually or in groups. These resources can in turn be easily retrieved via the search and recommendation services of the SSS.
As shown in Figure 1, the resulting services are exploited in various Layers tools (Bits & Pieces / Discussion Tool, LivingDocuments, Ach so!, Learning Toolbox, SSS Dashboard and KnowBrain) that support different perspectives on informal learning.
Changed development practices
The SSS provides client-side tool developers with an easy-to-use service framework for informal learning at the workplace. Thus, developers can focus on the user-interface parts of their tools rather than implementing individual backend solutions. This in turn leads to better tools with lower barriers for unexperienced users.
Ease of integration
Via its flexible service interfaces, the SSS eases the integration of additional features for tool developers. Furthermore, the SSS fosters the integration of tools to complex tool suites via providing a common backend infrastructure (see e.g., the Healthcare suite consisting of Bits and Pieces / Discussion Tool and Living Documents).
Links to other sections
- Infrastructure
Further readings
GitHub repository: https://github.com/learning-layers/SocialSemanticServer
Web site describing our research: http://sna.know-center.tugraz.at/
Slides presented by Tobias Ley at the third Layers review meeting in Luxembourg about the support of the SSS for Layers tools in Healthcare and Construction:
References
- M. Eraut, “Non-formal learning and tacit knowledge in professional work,” British journal of educational psychology, vol. 70, no. 1, pp. 113–136, 2000.
- A. Ruiz-Calleja, S. Dennerlein, V. Tomberg, T. Ley, D. Theiler, and E. Lex, “Integrating data across workplace learning applications with a social semantic infrastructure,” in Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Web-based Learning (ICWL 2015), Guangzhou, China, 2015, pp. 208–217. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-25515-6_19
- A. Ruiz-Calleja, S. Dennerlein, V. Tomberg, K. Pata, T. Ley, D. Theiler, and E. Lex, “Supporting Learning Analytics for Informal Workplace Learning with a Social Semantic Server,” in Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Tecnology Enhanced Learning (EC-TEL 2015), Toledo, Spain, 2015, pp. 634–637. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-24258-3_76
